 Contraception
Contraception
There are many methods of contraception, don’t be put off if the first type you use isn’t quite right – you can try another. Our information pages will help you determine which contraception method is best for you and you can talk through the options with our sexual health team.
If you have any questions or would like to explore one of the below methods of contraception further, please contact the team between 9am-5pm Monday – Thursday or 9am – 1pm on Fridays on 01432 483693 / 0800 7720478.
You can find out about Long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) options here.
Some Facts
- Contraception is free
- Only condoms help to prevent Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI’S)
- All methods of contraception work by either stopping the women’s egg (ova) or the man’s sperm from meeting or by preventing the release of the egg
- There isn’t a single method that is suitable for all women, and they are not free from side effects
- Women often use different methods during the course of their sexual lives, for different reasons
- Choosing the method that’s right for you may depend on how reliable it is, how it will affect you, as well as whether you have any medical conditions that may limit your choice.
We can talk to you about the choices available, and we will take a detailed medical history that will identify if any of the methods are not suitable.
The NHS choices website provides information about the many methods of contraception that are available in our service. The FPA is also a really good source of information relating to sexual health and contraception
- condoms
- combined pill
- female condoms
- natural family planning (fertility awareness)
- progestogen-only pill
There are also 2 permanent methods, which are not available in our service, but your own GP will be able to refer you to the hospital
 In an emergency
In an emergency
If you have had unprotected sex, (not used any method of contraception) or if the contraception you have used has failed you may be at risk of getting pregnant. Please don’t just ignore the risk, we can help. Contact us or your own GP as soon as possible after the unprotected sex, the sooner you seek help the more likely it is that we can help you to prevent a pregnancy.
The following pharmacies also currently provide Emergency Hormonal Contraception (EHC). Please ring and check that this is available before you attend:
- Boots Hereford, 42-43 Bewell Street, Hereford, HR4 9AA – 01432 274941
- Boots Ledbury, 9 High Street, Ledbury, HR8 1DS – 01531 632687
- Boots Leominster, 18 Corn Square, Leominster, HR6 8LR – 01568 612721
- Boots Ross-On-Wye, 5 Market Place, Ross-On-Wye, HR9 5NX – 01989 562798
- Bromyard Pharmacy, 35 High St, Bromyard, HR7 4AF – 01885 483291
- Chandos Pharmacy, 2-3 Chandos House, 46 St Owen Street , Hereford, HR1 2PR – 01432 272065
- Chave & Jackson Pharmacy, 6-7, Broad Street , Hereford, HR4 9AE – 01432 272152
- Day Lewis Pharmacy – 96 Grandstand Road, Hereford, HR4 9NR – 01432 343121
- Day Lewis Pharmacy – No 2 Sear House, Bye Street, Ledbury, HR8 2AA – 01531 632693
- Healthpoint Colwall Pharmacy, Fletton House, Walwyn Road, Colwall, WR13 6QG – 01684 540246
- Leominster Pharmacy, 21-23 West St, Leominster HR6 8EP – 01568 615429
- Lloyds Pharmacy – 10 King St, Hereford, HR4 9BW – 01432 371512
- Morrisons Pharmacy, Station Approach, Hereford, HR1 1DN – 01432 341007
- Sainsburys Pharmacy (Lloyds) – Barton Yard, Whitecross Road, Hereford, HR4 0AG – 01432 375979
- Taylors Pharmacy – 1-2 St Owens Mews, St Owens Street, Hereford, HR1 2JB – 01432 264242
- W S and B Rees Pharmacy – 20 High Street, Leominster, HR6 8LZ – 01568 612306
- Westfield Walk Pharmacy – Westfield Walk , Leominster, HR6 8HD – 01568 610399
The IUD can be fitted up to 5 days after unprotected sex, or up to 5 days after the earliest time you could have ovulated, for it to be effectiveYou need to take the emergency contraceptive pill within 3 days (Levonelle) or 5 days (ellaOne) of unprotected sex for it to be effective – the sooner you take it, the more effective it’ll be.There are two main types of contraception you can use in an emergency, the pill, (2 different types) and the Intra- uterine Contraceptive device (IUD) or COIL, which needs to be fitted into the uterus by a specially trained doctor or nurse.If for some reason, you don’t seek help straight away and you think, ‘it’s too late’, please still come to see us, there may still be something we can do. Emergency Contraception -PillsEmergency Contraception – Intra- uterine Contraceptive device/COIL
|
 Male and Female condoms
Male and Female condoms
If you’re ready to start to thinking about having sex, or already having sex, then it’s a good time to think about how you will keep yourself sexually healthy. Condoms are the only way to help prevent the spread of infection. That’s really important if you don’t want to catch or spread an STI (Sexually Transmitted Infection) like chlamydia, gonorrhoea or HIV. They also are a good way to prevent pregnancy.
Male Condoms
How effective is the male Condom?
Condoms are 98% effective if used correctly. This means 2 out of 100 women will become pregnant in one year when male condoms are used as contraception.
How do I use the condom?
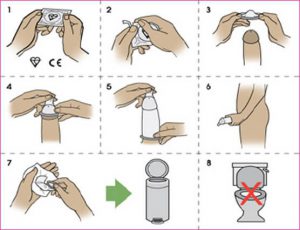
- Condoms have an expiry date; check your condom is in date and that it has a CE and KITE mark
- Condom packets usually have two straight edges and two serrated edges; tear straight down, serrated edge to serrated edge
- Place the condom on to the erect penis
- Pinch the top of the condom as you put it on. This leaves space for air (to prevent the condom splitting and space for the ejaculation fluid)
- Roll the condom right down to the base of the penis
- If it won’t roll onto your penis properly, you may have it the wrong way round the roll needs to be on the outside. If this happens don’t just turn it over sperm may be present on the tip of your penis, just use another condom
- Keep hold of the condom as you withdraw and remove it once you’re away from your partner
- Wrap the used condom in a tissue
- Place it in a bin
- Do not flush condoms down the toilet
If you are using gels or other lubricants they need to be water-based, oil-based versions can damage the latex condom, making it more likely to split.
If the condom splits, it will not have protected you and if you are using it for prevention of pregnancy, you will need Emergency Contraception.
Click here for more information on male condoms
Female Condoms
The female condom is a soft, loose fitting pouch with a ring on each end. Unlike a male condom you can put the female condom in ahead of time, before sex begins.
How effective is the female Condom?
The female condom is slightly less effective than the male condom and is 95% effective if used correctly. This means 5 out of 100 women will become pregnant in one year when female condoms are used as contraception.
How do I use the condom?
- As with male condoms you need to check the expiry date on the package, and then open it carefully
- If you’re putting the condom in your anus, remove the inner ring. If you’re putting the condom in your vagina, leave the ring in
- Relax and get into a comfortable position to insert the condom, standing with one foot on a chair, lying down, or squatting
- If it’s going in your vagina, squeeze together the sides of the inner ring at the closed end of the condom and slide it in like a tampon. Pushing the inner ring into your vagina as far as it can go
- If it’s going in your anus, just push the condom in with your finger
- Make sure the condom isn’t twisted. Pull out your finger and let the outer ring hang about an inch outside the vagina or anus
- Hold the condom open as the penis or sex toy is going into the condom to make sure it doesn’t slip to the side between the condom and your vagina or anus
- Gently pull it out of your vagina or anus, being careful not to spill the semen if there is any
- Throw it away in the bin
Click here for more information on female condoms
 The Combined Pill
The Combined Pill
This is a pill that contains synthetic hormones that are similar to the ones fertile women naturally produce, in their ovaries called progesterone and oestrogen. There are different types of pills that have slightly different levels of the hormones.
How does it work?
It works by preventing a woman from ovulating (releasing an egg).
It also thickens the mucous that sits in the cervix (neck of the womb) making it difficult for the sperm to swim through and it makes the lining of the uterus (womb) thin, so the environment isn’t suitable for implantation of an egg.
How effective is it?
When taken correctly, the pill is over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. As with most methods, the pill will work really well to prevent a pregnancy, but doesn’t protect you from sexually transmitted infections, so you will need to use condoms as well.
What are the side effects?
Blood Clots
The oestrogen in the pill may cause your blood to clot more readily. The risk of getting a blood clot is very small. But If a blood clot develops, it could cause: deep vein thrombosis (clot in your leg) , pulmonary embolus (clot in your lung) or even more rarely a stroke or heart attack.
Breast Cancer
Research is still ongoing into the link between breast cancer and the pill. Current research suggests that users of all types of hormonal contraception have a slightly higher chance of being diagnosed with breast cancer compared to women who do not use them. However, 10 years after you stop taking the pill, your risk of breast cancer goes back to normal.
The combined pill can cause temporary side effects, too at first, like headaches, nausea, breast tenderness and mood swings – if these do not go after a few months, it may help to change to a different type of pill
The Combined pill can sometimes increase your blood pressure, so we will check this soon after you have been prescribed the pill.
What happens if I miss taking one of my pills?
The pill is only 99% effective if its taken properly If you miss a pill or pills, or you start a pack late, it can make the pill less effective at preventing a pregnancy.
The chance of getting pregnant after missing a pill or pills depends on: when the pills are missed and how many pills are missed.
What to do if you miss a combined pill.
Find out what to do if you miss a combined pill here.
What do I do if I have sickness and or diarrhoea?
If you vomit within two hours of taking the combined pill, it may not have had time to be absorbed into your bloodstream. Take another pill straight away and the next pill at your usual time.
If you continue to be sick, keep using another form of contraception until you’ve taken the pill for another seven days without vomiting.
Very severe diarrhoea (six to eight watery stools in 24 hours) may also mean that the pill doesn’t work properly. Keep taking your pill as normal, but use additional contraception, such as condoms, while you have diarrhoea and for two days after recovering. Also do seek medical help if the diarrhoea and vomiting is this severe.
If you are in any doubt about what to do, don’t ignore it, just contact us on 0800 7720478
Click here for more information on the combined pill
 Progestogen Only Pill (POP)
Progestogen Only Pill (POP)
The progestogen only pill (POP) contains only one hormone, progestogen. Unlike the COC pill, POPs need to be taken every day without a break. Once one pack has been finished, a new one can be started straight away. It’s a useful alternative for women that can’t have the combined pill because of the Oestrogen.
How effective is the POP?
The POP is 99% effective if taken correctly.
How does it work?
The POP thickens the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from meeting the egg whilst also thinning the lining of the womb. In some women, ovulation also stops.
What are the disadvantages?
Missing pills, vomiting or severe diarrhoea may make the pill less effective.
Periods may stop or be irregular, lighter or more frequent. It is not a problem if they stop; it is because it’s working well to keep the lining in your uterus (womb) thin, so that there is little or nothing to shed.
Click here for more information on the progestogen-only pill
 Pregnant and unsure of what to do?
Pregnant and unsure of what to do?
Finding out you are pregnant, when it wasn’t planned can be very distressing. For some women they may be unsure what to do next. You can contact us or speak to your own doctor for advice about the options.
If you feel that having a pregnancy at this time is not right for you, they can also refer you on to an abortion service provider, who will be able to give you more advice, to help you make the right choice for you and your circumstances.
If you are in any doubt about what to do, contact us on 0800 7720478
(All abortion services are free on the NHS)
 Contraception
Contraception
There are many methods of contraception, don’t be put off if the first type you use isn’t quite right – you can try another. Our information pages will help you determine which contraception method is best for you and you can talk through the options with our sexual health team.
If you have any questions or would like to explore one of the below methods of contraception further, please contact the team between 9am-5pm Monday – Thursday or 9am – 1pm on Fridays on 01432 483693 / 0800 7720478.
You can find out about Long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) options here.
Some Facts
- Contraception is free
- Only condoms help to prevent Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI’S)
- All methods of contraception work by either stopping the women’s egg (ova) or the man’s sperm from meeting or by preventing the release of the egg
- There isn’t a single method that is suitable for all women, and they are not free from side effects
- Women often use different methods during the course of their sexual lives, for different reasons
- Choosing the method that’s right for you may depend on how reliable it is, how it will affect you, as well as whether you have any medical conditions that may limit your choice.
We can talk to you about the choices available, and we will take a detailed medical history that will identify if any of the methods are not suitable.
The NHS choices website provides information about the many methods of contraception that are available in our service. The FPA is also a really good source of information relating to sexual health and contraception
- condoms
- combined pill
- female condoms
- natural family planning (fertility awareness)
- progestogen-only pill
There are also 2 permanent methods, which are not available in our service, but your own GP will be able to refer you to the hospital
 In an emergency
In an emergency
If you have had unprotected sex, (not used any method of contraception) or if the contraception you have used has failed you may be at risk of getting pregnant. Please don’t just ignore the risk, we can help. Contact us or your own GP as soon as possible after the unprotected sex, the sooner you seek help the more likely it is that we can help you to prevent a pregnancy.
The following pharmacies also currently provide Emergency Hormonal Contraception (EHC). Please ring and check that this is available before you attend:
- Boots Hereford, 42-43 Bewell Street, Hereford, HR4 9AA – 01432 274941
- Boots Ledbury, 9 High Street, Ledbury, HR8 1DS – 01531 632687
- Boots Leominster, 18 Corn Square, Leominster, HR6 8LR – 01568 612721
- Boots Ross-On-Wye, 5 Market Place, Ross-On-Wye, HR9 5NX – 01989 562798
- Bromyard Pharmacy, 35 High St, Bromyard, HR7 4AF – 01885 483291
- Chandos Pharmacy, 2-3 Chandos House, 46 St Owen Street , Hereford, HR1 2PR – 01432 272065
- Chave & Jackson Pharmacy, 6-7, Broad Street , Hereford, HR4 9AE – 01432 272152
- Day Lewis Pharmacy – 96 Grandstand Road, Hereford, HR4 9NR – 01432 343121
- Day Lewis Pharmacy – No 2 Sear House, Bye Street, Ledbury, HR8 2AA – 01531 632693
- Healthpoint Colwall Pharmacy, Fletton House, Walwyn Road, Colwall, WR13 6QG – 01684 540246
- Leominster Pharmacy, 21-23 West St, Leominster HR6 8EP – 01568 615429
- Lloyds Pharmacy – 10 King St, Hereford, HR4 9BW – 01432 371512
- Morrisons Pharmacy, Station Approach, Hereford, HR1 1DN – 01432 341007
- Sainsburys Pharmacy (Lloyds) – Barton Yard, Whitecross Road, Hereford, HR4 0AG – 01432 375979
- Taylors Pharmacy – 1-2 St Owens Mews, St Owens Street, Hereford, HR1 2JB – 01432 264242
- W S and B Rees Pharmacy – 20 High Street, Leominster, HR6 8LZ – 01568 612306
- Westfield Walk Pharmacy – Westfield Walk , Leominster, HR6 8HD – 01568 610399
The IUD can be fitted up to 5 days after unprotected sex, or up to 5 days after the earliest time you could have ovulated, for it to be effectiveYou need to take the emergency contraceptive pill within 3 days (Levonelle) or 5 days (ellaOne) of unprotected sex for it to be effective – the sooner you take it, the more effective it’ll be.There are two main types of contraception you can use in an emergency, the pill, (2 different types) and the Intra- uterine Contraceptive device (IUD) or COIL, which needs to be fitted into the uterus by a specially trained doctor or nurse.If for some reason, you don’t seek help straight away and you think, ‘it’s too late’, please still come to see us, there may still be something we can do. Emergency Contraception -PillsEmergency Contraception – Intra- uterine Contraceptive device/COIL
|
 Male and Female condoms
Male and Female condoms
If you’re ready to start to thinking about having sex, or already having sex, then it’s a good time to think about how you will keep yourself sexually healthy. Condoms are the only way to help prevent the spread of infection. That’s really important if you don’t want to catch or spread an STI (Sexually Transmitted Infection) like chlamydia, gonorrhoea or HIV. They also are a good way to prevent pregnancy.
Male Condoms
How effective is the male Condom?
Condoms are 98% effective if used correctly. This means 2 out of 100 women will become pregnant in one year when male condoms are used as contraception.
How do I use the condom?
- Condoms have an expiry date; check your condom is in date and that it has a CE and KITE mark
- Condom packets usually have two straight edges and two serrated edges; tear straight down, serrated edge to serrated edge
- Place the condom on to the erect penis
- Pinch the top of the condom as you put it on. This leaves space for air (to prevent the condom splitting and space for the ejaculation fluid)
- Roll the condom right down to the base of the penis
- If it won’t roll onto your penis properly, you may have it the wrong way round the roll needs to be on the outside. If this happens don’t just turn it over sperm may be present on the tip of your penis, just use another condom
- Keep hold of the condom as you withdraw and remove it once you’re away from your partner
- Wrap the used condom in a tissue
- Place it in a bin
- Do not flush condoms down the toilet
If you are using gels or other lubricants they need to be water-based, oil-based versions can damage the latex condom, making it more likely to split.
If the condom splits, it will not have protected you and if you are using it for prevention of pregnancy, you will need Emergency Contraception.
Click here for more information on male condoms

Female Condoms
The female condom is a soft, loose fitting pouch with a ring on each end. Unlike a male condom you can put the female condom in ahead of time, before sex begins.
How effective is the female Condom?
The female condom is slightly less effective than the male condom and is 95% effective if used correctly. This means 5 out of 100 women will become pregnant in one year when female condoms are used as contraception.
How do I use the condom?
- As with male condoms you need to check the expiry date on the package, and then open it carefully
- If you’re putting the condom in your anus, remove the inner ring. If you’re putting the condom in your vagina, leave the ring in
- Relax and get into a comfortable position to insert the condom, standing with one foot on a chair, lying down, or squatting
- If it’s going in your vagina, squeeze together the sides of the inner ring at the closed end of the condom and slide it in like a tampon. Pushing the inner ring into your vagina as far as it can go
- If it’s going in your anus, just push the condom in with your finger
- Make sure the condom isn’t twisted. Pull out your finger and let the outer ring hang about an inch outside the vagina or anus
- Hold the condom open as the penis or sex toy is going into the condom to make sure it doesn’t slip to the side between the condom and your vagina or anus
- Gently pull it out of your vagina or anus, being careful not to spill the semen if there is any
- Throw it away in the bin
Click here for more information on female condoms
 The Combined Pill
The Combined Pill
This is a pill that contains synthetic hormones that are similar to the ones fertile women naturally produce, in their ovaries called progesterone and oestrogen. There are different types of pills that have slightly different levels of the hormones.
How does it work?
It works by preventing a woman from ovulating (releasing an egg).
It also thickens the mucous that sits in the cervix (neck of the womb) making it difficult for the sperm to swim through and it makes the lining of the uterus (womb) thin, so the environment isn’t suitable for implantation of an egg.
How effective is it?
When taken correctly, the pill is over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. As with most methods, the pill will work really well to prevent a pregnancy, but doesn’t protect you from sexually transmitted infections, so you will need to use condoms as well.
What are the side effects?
Blood Clots
The oestrogen in the pill may cause your blood to clot more readily. The risk of getting a blood clot is very small. But If a blood clot develops, it could cause: deep vein thrombosis (clot in your leg) , pulmonary embolus (clot in your lung) or even more rarely a stroke or heart attack.
Breast Cancer
Research is still ongoing into the link between breast cancer and the pill. Current research suggests that users of all types of hormonal contraception have a slightly higher chance of being diagnosed with breast cancer compared to women who do not use them. However, 10 years after you stop taking the pill, your risk of breast cancer goes back to normal.
The combined pill can cause temporary side effects, too at first, like headaches, nausea, breast tenderness and mood swings – if these do not go after a few months, it may help to change to a different type of pill
The Combined pill can sometimes increase your blood pressure, so we will check this soon after you have been prescribed the pill.
What happens if I miss taking one of my pills?
The pill is only 99% effective if its taken properly If you miss a pill or pills, or you start a pack late, it can make the pill less effective at preventing a pregnancy.
The chance of getting pregnant after missing a pill or pills depends on: when the pills are missed and how many pills are missed.
What to do if you miss a combined pill.
Find out what to do if you miss a combined pill here.
What do I do if I have sickness and or diarrhoea?
If you vomit within two hours of taking the combined pill, it may not have had time to be absorbed into your bloodstream. Take another pill straight away and the next pill at your usual time.
If you continue to be sick, keep using another form of contraception until you’ve taken the pill for another seven days without vomiting.
Very severe diarrhoea (six to eight watery stools in 24 hours) may also mean that the pill doesn’t work properly. Keep taking your pill as normal, but use additional contraception, such as condoms, while you have diarrhoea and for two days after recovering. Also do seek medical help if the diarrhoea and vomiting is this severe.
If you are in any doubt about what to do, don’t ignore it, just contact us on 0800 7720478
Click here for more information on the combined pill
 Progestogen Only Pill (POP)
Progestogen Only Pill (POP)
The progestogen only pill (POP) contains only one hormone, progestogen. Unlike the COC pill, POPs need to be taken every day without a break. Once one pack has been finished, a new one can be started straight away. It’s a useful alternative for women that can’t have the combined pill because of the Oestrogen.
How effective is the POP?
The POP is 99% effective if taken correctly.
How does it work?
The POP thickens the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from meeting the egg whilst also thinning the lining of the womb. In some women, ovulation also stops.
What are the disadvantages?
Missing pills, vomiting or severe diarrhoea may make the pill less effective.
Periods may stop or be irregular, lighter or more frequent. It is not a problem if they stop; it is because it’s working well to keep the lining in your uterus (womb) thin, so that there is little or nothing to shed.
Click here for more information on the progestogen-only pill
 Pregnant and unsure of what to do?
Pregnant and unsure of what to do?
Finding out you are pregnant, when it wasn’t planned can be very distressing. For some women they may be unsure what to do next. You can contact us or speak to your own doctor for advice about the options.
If you feel that having a pregnancy at this time is not right for you, they can also refer you on to an abortion service provider, who will be able to give you more advice, to help you make the right choice for you and your circumstances.
If you are in any doubt about what to do, contact us on 0800 7720478
(All abortion services are free on the NHS)


